Meniscus Injuries and Treatment Options
Meniscus tissue is vital for the healthy functioning of the knee joint. However, meniscus injuries are quite common due to sports injuries, traumas or age-related degeneration. When left untreated, meniscus injuries can lead to problems such as pain, swelling and limitation of movement in the knee joint. You can learn more about the causes, symptoms and treatment options for meniscus injuries.
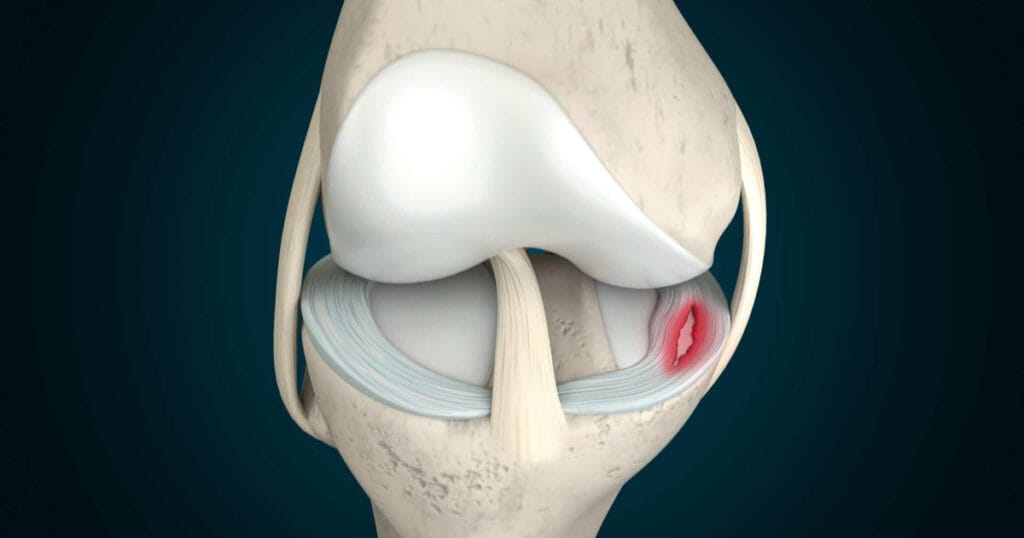
What is a meniscus and why is it important?
The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage tissue located between the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone) in the knee joint. Each knee has two menisci, the inner (medial) and outer (lateral). The main functions of meniscus tissue are as follows:
- It balances the load on the knee joint and acts as a shock absorber.
- Provides stability of the joint.
- Supports knee movements.
Causes of Meniscus Injuries
Meniscus injuries usually occur in the following situations:
- Traumatic Injuries: The meniscus may tear in cases such as sudden rotation, load on the knee or fall during sports.
- Age-related Degeneration: Meniscus tissue weakens with age and can be damaged more easily.
- Overuse: Continuous knee bending or strenuous activities can cause the meniscus to wear out.
Symptoms of Meniscus Injury
The most common symptoms of a meniscus injury are:
- Pain in the knee, especially increased pain during movement
- Swelling or stiffness in the knee
- Locking sensation in the knee joint
- Sticking or snapping noise during movement
- Difficulty in full flexion or extension of the knee joint
Treatment Options for Meniscus Injuries
In the treatment of meniscal injuries, different approaches can be applied depending on the type and extent of the damage and the age of the patient. Treatment options are generally classified as follows:
1. Preventive and Conservative Treatments
- Rest: It is recommended to avoid activities to reduce the load on the knee.
- Ice Application: Ice packs can be applied at regular intervals to reduce swelling and pain.
- Physiotherapy: Special exercises are performed to increase muscle strength and restore joint mobility.
- Drug Therapy: Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs can be used to control inflammation and pain.
2. Injection Treatments
- It is especially preferred in Type 2 meniscus damage.
- PRP – PRGF – Stem cell: Regenerative injections can be made to support meniscal healing.
- Hyaluronic Acid: It can be used to increase the lubrication of the joint and reduce pain.
3. Surgical Treatments
Depending on the size and location of the meniscus tear, surgical intervention may be necessary, especially in type 3 and type 4 tears. Surgical methods are usually applied with arthroscopic techniques:
- Meniscal Repair: It is the repair of the tear by suturing. It is generally preferred in young and active patients.
- Meniscectomy: Partial or complete removal of the damaged meniscus tissue. The remaining meniscus tissue is preserved as much as possible.
- Meniscus transplantation: In cases of severe meniscal loss, transplantation of donor meniscal tissue can be performed.
Postoperative Rehabilitation
A successful rehabilitation process after surgery directly affects the success of meniscus treatment. In this process
- The range of motion of the knee is increased with physiotherapy exercises.
- Regular exercise programmes are applied to restore muscle strength.
- The rehabilitation process usually lasts between 6-12 weeks.
Ways to Prevent Meniscus Injuries
- Use correct techniques and wear appropriate equipment when doing sports.
- Increase joint stability by doing exercises that strengthen the knee muscles.
- Avoid sudden rotation or forceful movements.
- Maintain a healthy weight to avoid overloading your joints.
Meniscus injuries can be successfully managed with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Especially early interventions are of great importance in maintaining the health of the knee joint. If you have complaints about meniscus injuries, it is important to consult a specialist for correct diagnosis and treatment.