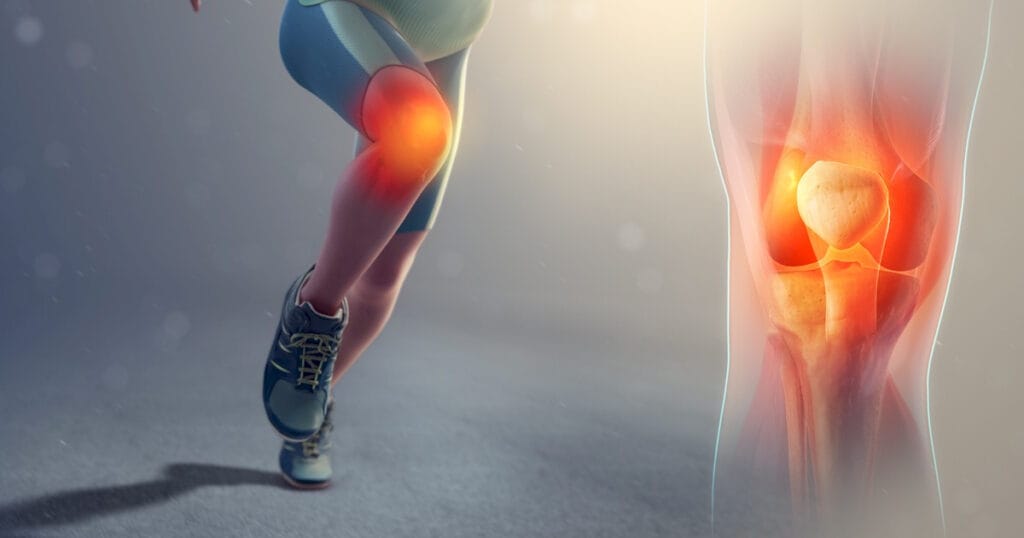
Patellofemoral Joint and Sports Injuries
The patellofemoral joint is an important part of the knee joint and can be frequently injured, especially in athletes. Repetitive movements such as running, jumping, stopping suddenly and changing direction can cause pain and loss of function in this joint. Sports injuries affecting the patellofemoral joint can lead to long-term problems if left untreated. In this article, we will examine the structure of the patellofemoral joint, sports injuries and treatment options.
What is the Patellofemoral Joint?
The patellofemoral joint is the joint located between the kneecap (patella) and the thighbone (femur). This joint allows the patella to move smoothly in the groove on the femur during flexion and extension of the knee. Healthy functioning of the patellofemoral joint supports the stability and mobility of the knee joint.
Causes of Patellofemoral Joint Injuries
The main causes of patellofemoral joint injuries are:
- Repetitive Strains: Excessive load on the joint during sports activities such as running, jumping or cycling.
- Traumas: Injuries caused by direct blows to the kneecap or sudden movements.
- Muscle Imbalances: Imbalances in the quadriceps and hamstring muscles can disrupt the proper alignment of the patella.
- Structural Problems: Dislocation of the patella out of its normal position (patella dislocation) or congenital abnormalities in the knee structure.
Symptoms of Patellofemoral Joint Injuries
- Pain in the front of the knee (patellofemoral pain syndrome)
- Increased pain when climbing stairs or squatting
- A feeling of stiffness in the knee after sitting for a long time
- A feeling of popping or rubbing during patella movement
- Swelling or tenderness in the knee
Important Conditions Related to Sports Injuries
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS): Also known as “Runner’s knee”. It is common in runners, cyclists and those who do sports that require jumping.
- Patella Dislocation (Kneecap dislocation): It is the dislocation of the patella from the femoral groove. It usually occurs as a result of sudden trauma.
- Chondromalacia Patella: It is the softening and damage of the cartilage tissue under the patella. It is common in athletes.
Treatment Options
Treatment of patellofemoral joint injuries is planned depending on the type and severity of the injury.
1. Conservative Treatment
- Rest and Activity Change: It is recommended to limit activities for the injury to heal.
- Ice Application: Regular ice application can be done to reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Physical Therapy: Special exercises are applied to strengthen the quadriceps, hamstring and hip muscles. In addition, flexibility and balance exercises are done to support the proper movement of the patella.
- Knee Brace and Taping: Special knee braces or taping techniques can be used to increase the alignment and stability of the kneecap.
2. Injection Treatments
- PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma): It can be applied to accelerate the healing of injured tissue.
- Hyaluronic Acid Injection: It reduces pain by increasing the lubrication of the joint.
3. Surgical Treatment
- Arthroscopic Surgery: It is a minimally invasive method for repairing damage to the patellofemoral joint.
- Soft Tissue Corrections: Surgical intervention may be required to provide alignment and stability of the patella. (MPFL repair)
- Cartilage Repair: In cases such as chondromalacia patella, damaged cartilage is treated.
Ways to Prevent Patellofemoral Joint Injuries
- Provide Muscle Balance: Do regular exercises that strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings and hip muscles.
- Using Correct Technique: It is important to learn the correct form and technique in sports activities.
- Flexibility Exercises: You can reduce the risk of injury by increasing the flexibility of muscles and ligaments.
- Use Appropriate Shoes: Choose appropriate shoes that support the knee joint during sports.
- Progress Slowly: Instead of starting sports activities suddenly, gradually increase the intensity.
Patellofemoral joint injuries can be successfully managed with the right treatment and precautions. Especially in athletes, early diagnosis and appropriate rehabilitation programs are critical in maintaining joint health. If you are experiencing problems such as knee pain or limited movement, you can see a specialist and evaluate your condition.